|
Oaks Click here to choose Pedunculate Oak (Quercus robur) Click here to choose Sessile Oak (Quercus petraea) Click here to choose Turkey Oak (Quercus cerris) |
|
Simple
Lobed Alternate |
||
|
|
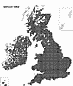
The alternate leaves are 5-12 cm long and have 3-5 various sized lobes on each side. They have 'ears' at the base and only a few hairs beneath, when young. The leaf stalk is very short or absent. ID check
Facts
|
|
|
Simple
Lobed Alternate |
||
|
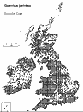
The alternate leaves, 5-12 cm long, have 5-6 various sized lobes on either side, and no ears at the base which narrows gradually into a leaf stalk 10-25 mm long. The leaves have persistent hairs at the base of the mid-rib beneath. ID check
Facts
|
||
|
Simple
Lobed Alternate |
||
|
The alternate leaves are 5-10 cm long, with 7-8 various sizes of pointed lobes on each side. The leaves are paler below and hairy on both surfaces when they are young. They have no 'ears' at the base and narrow to a leaf stalk 10-25 mm long, at the base of which are pale, narrow stipules. ID Check
Facts
|
||
Return to Index Page